Being long exposed to tough conditions such as wind, rain, and sunlight, fiberglass antennas which are designed to be used out of doors, face a lot of wear and tears. Thus, the requirements concerning the materials, the processes, as well as the testing standards are targets that are set for outdoor products and differ significantly from indoor products.
1. Selection of Fiberglass Tubes
Fiberglass tubes serve as the basic building components of fiberglass antennas, effectively determining the functioning and endurance of the antennas. As for now, the main molding technologies used for fiberglass tubes include:
Pultrusion Molding:
Fiberglass strands are impregnated with resin, heated and cured through molds, and then extruded. this process embodies high efficiency whilst maintaining quality, making it useful for mass-production processes despite its vulnerability to long transverse cracks under stress.
Filament Winding:
Fiberglass strands are wound on a mandrel and cured. This process allows the production of various of fiberglass tube shapes and sizes; effective for small-batch production but is rather expensive.
Braiding:
During the casting process, the fibers are cast over the tube by a controlled pattern creating excellent axial strength circumferentially and longitudinally. Its rigidity and overall strength can be set to suit certain specifications while maintaining the process cost to be moderate. ABOOSTY uses this low-cost procedure to create long-lasting, seamless surfaces avoiding any cracks on it.
Injection Molding:
Molten fiberglass-reinforced plastic is injected into molds and cooled. This process is highly efficient, and quality-stable, making it ideal for mass production.
Blow Molding:
Molten fiberglass-reinforced plastic is shaped using blow molding machines. This process allows the production of various fiberglass tube shapes, suitable for small-batch production.
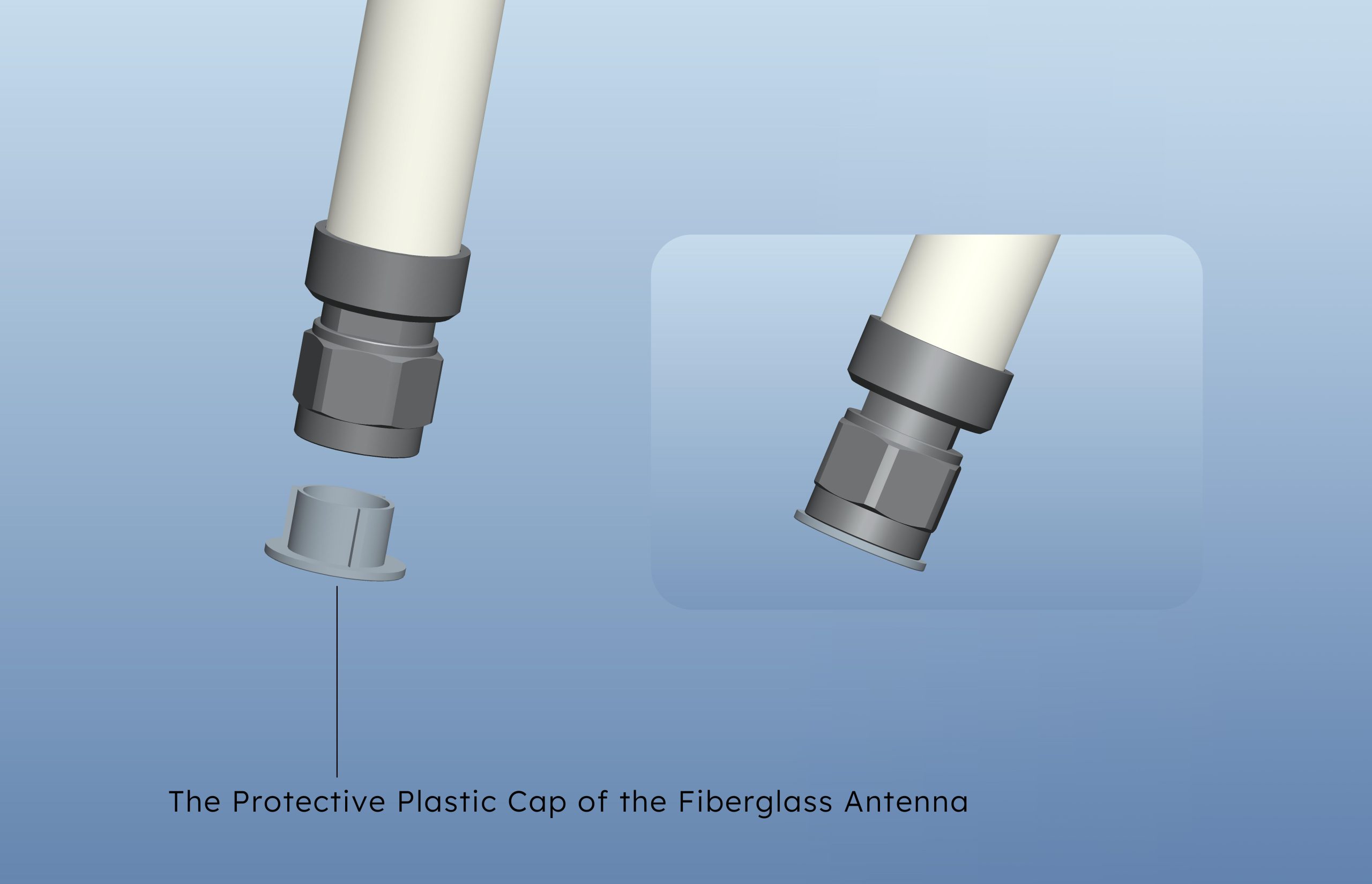
2. Selection of Protective Plastic Caps
Poor-quality caps turning yellow within a year can ruin the product’s aesthetics. Typically, ABS is used for
its strength, toughness, and ease of processing, but it has poor weather and oxidation resistance. Even
if special attention is paid to light factors when storing ABS particles, without adding additives, they
will still easily turn yellow under long-term exposure to sunlight, wind, and rain, and white ones are
no exception.
ABOOSTY uses ASA plastic instead, developed to address ABS’s shortcomings, maintaining
consistent color and stability even under prolonged outdoor exposure.

3. Tackling Venting Issues During Dispensing
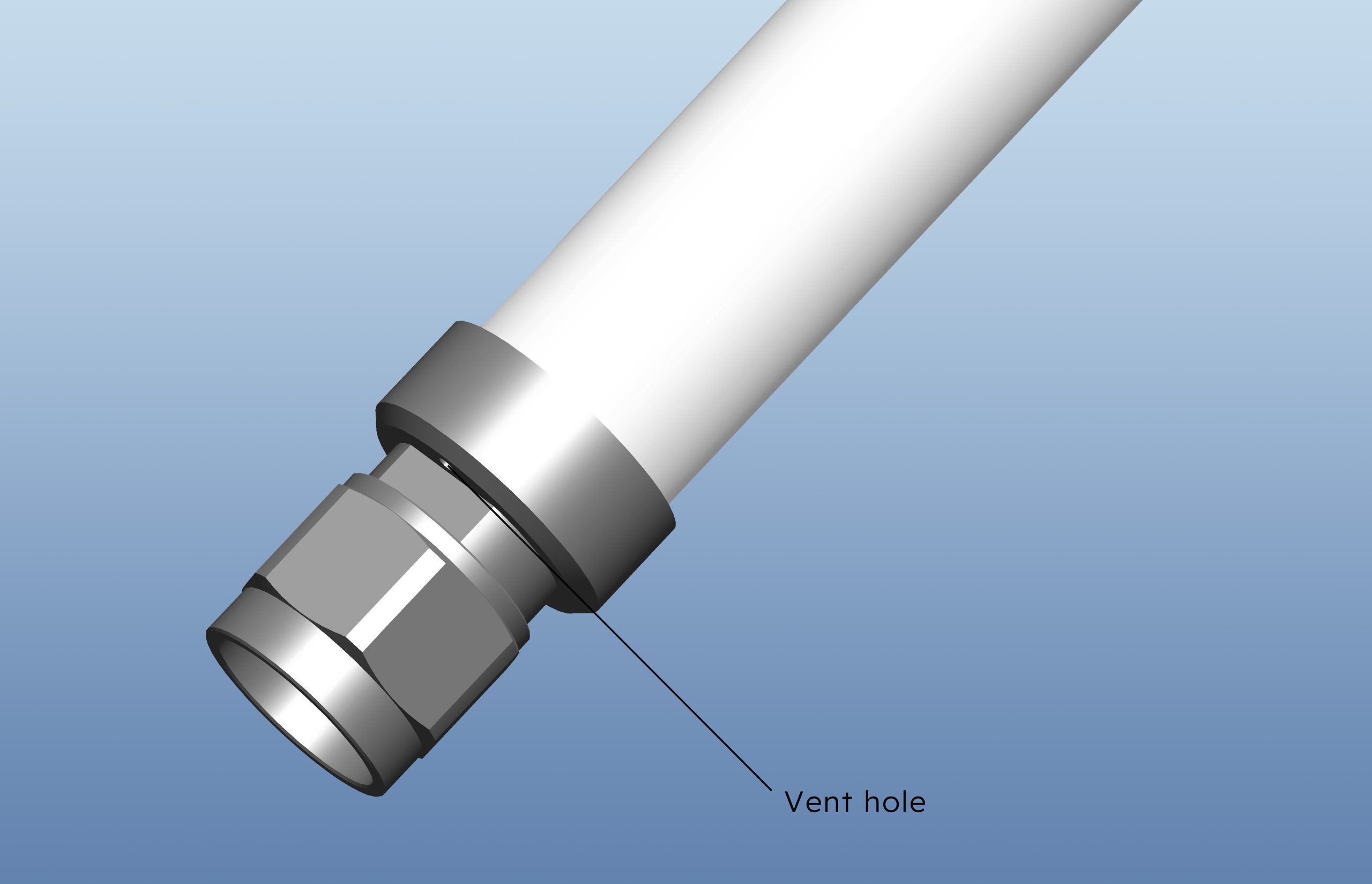
During glue dispensing, bubbles form due to trapped air which can affect the product’s appearance and waterproofing abilities. If the air bubbles occur in critical areas, the fluids may seep in, compromising their reliability and lifespan. Even worse are these air bubbles which could decrease the strength of the insulation and mechanical strength of the product.
These problems are avoided by Aboosty through the use of a venting hole placed at the N-type connector part which allows trapped air to be released during dispensing.
4. Anti-Vibration Measures
During small-batch testing, issues like fiberglass tube detachment and loose nuts were noted. Traditional
knurled nuts which were intended to to fasten these parts together couldn’t be fully
tightened
due to a lack of assisting tools and increased friction that made it unable to tighten them entirely by
hand.
This weakens the connection strength between the fiberglass tube and the N-type
connector.
In real-use cases subjected to external forces like vibration, it was
noticed that the
loose bond between the fiberglass tube and the N head resulted in the N head falling off and failure of
equipment which in extreme cases could lead to serious safety hazards.
Moreover, the detachment
of the
tube and the loosing of the screw sleeve may damage other parts, thus leading to increased maintenance
costs and
repair time.
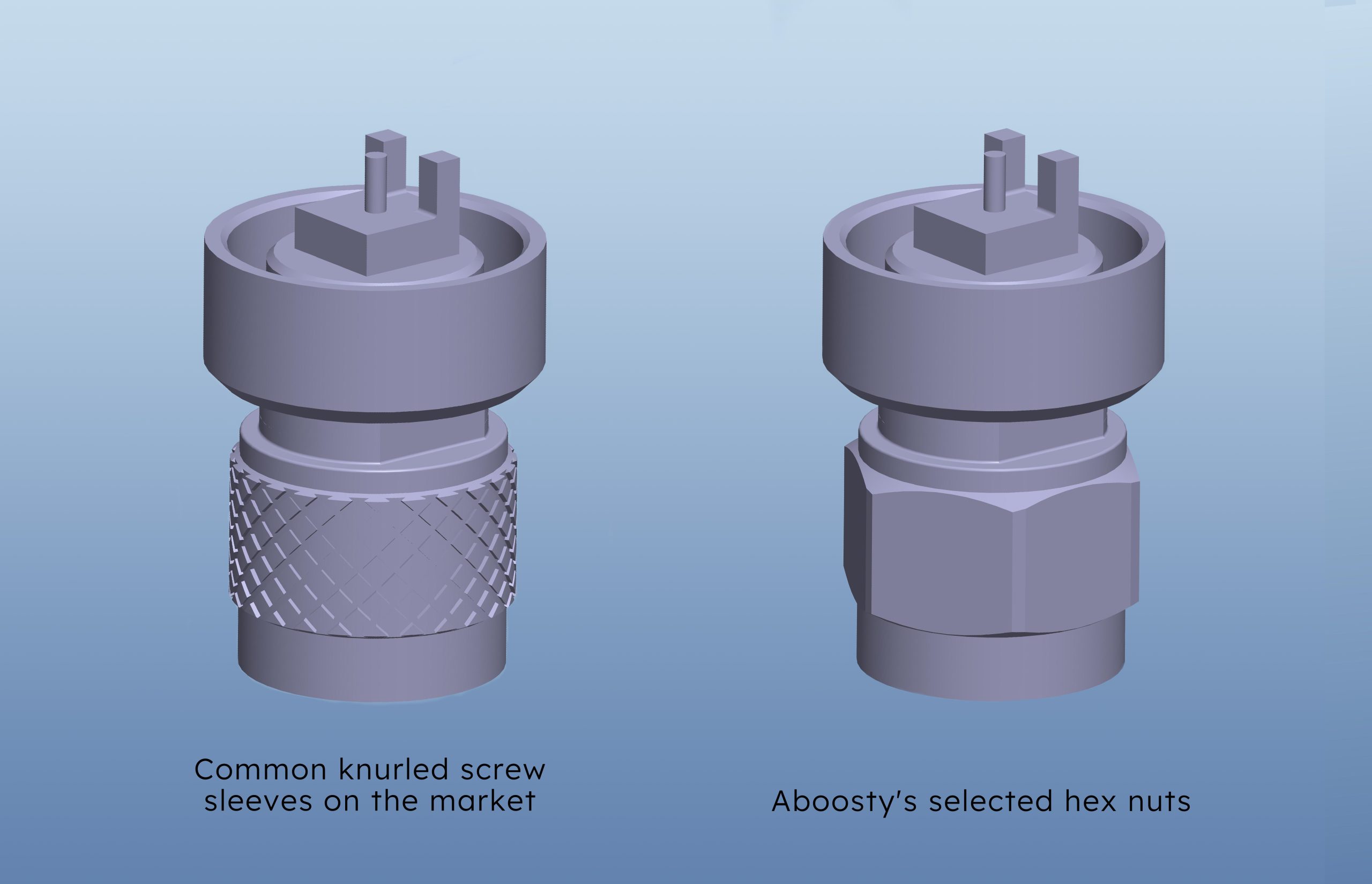
4.1 Using Tools for Controlled Tightening of Connectors:
Commonly used knurled screw sleeves in the market are typically hand-tightened, resulting in inconsistent force due to varying hand strength. The round knurled design also makes it difficult to fully tighten using external tools, leading to weak connections between the fiberglass tube and the N head, which can compromise signal transmission stability. ABOOSTY addresses this issue by replacing the knurled sleeves with hex nuts and defining the torque, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
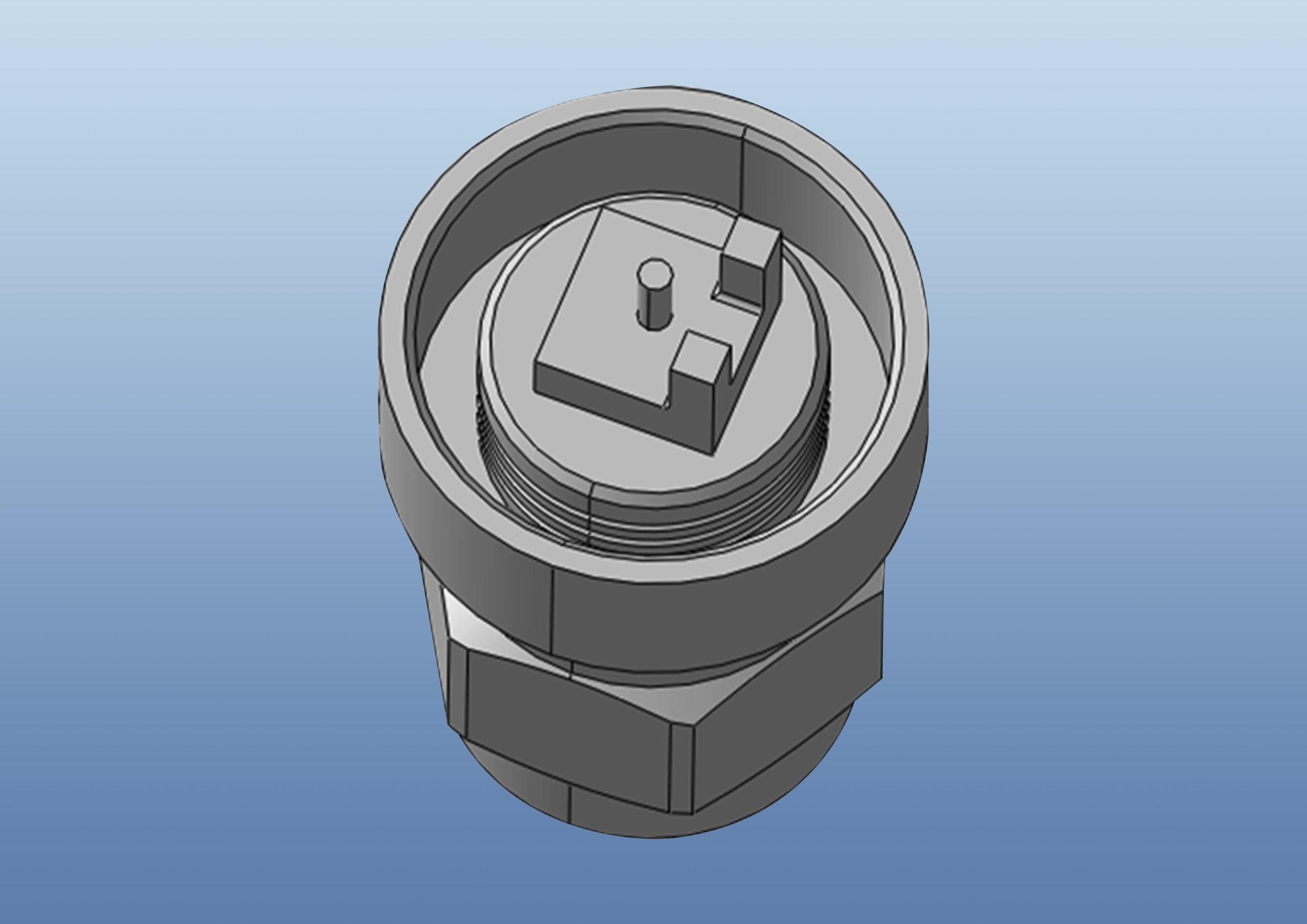
4.2. Enhanced Adhesion Involvement of the Overall Design:
Increased contact areas enable better bonding of adhesives, thereby increasing the strength of the connection. To deal with this problem, ABOOSTY embeds three adhesive grooves in the design. This ensures stronger bonding between the N head and the fiberglass tube. The additional adhesive eliminates the risk of tube detachment and screw sleeve loosening even when exposed to vibration.
Of course, tasks related to design development are not the only ones requiring particular attention – the selection of materials of high quality is also quite critical to the final product’s reliability. For example, it is essential to select the right adhesive to achieve the required level of bonding strength.
With extensive experience in the antenna industry for over 15 years, ABOOSTY focuses more on installing and securing the internal antenna within the fiberglass pipe during manufacturing that would stand up to the arbitrary movements and vibrations expected in most vehicle and industrial applications of wireless communications.
Your needs in terms of product reliability and performance will be fully satisfied by the overwhelming body of experience that we carry. Contact us to discuss and collaborate further!

4 Responses
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I need to to thank you for this very good read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you book marked to check out new things you post…
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.